Ghardaia
The wilaya of Ghardaïa is an administrative division located in southern Algeria, in the M'zab region. It is surrounded by the wilayas of Laghouat to the north, Ouargla to the east, and El Bayadh to the west.
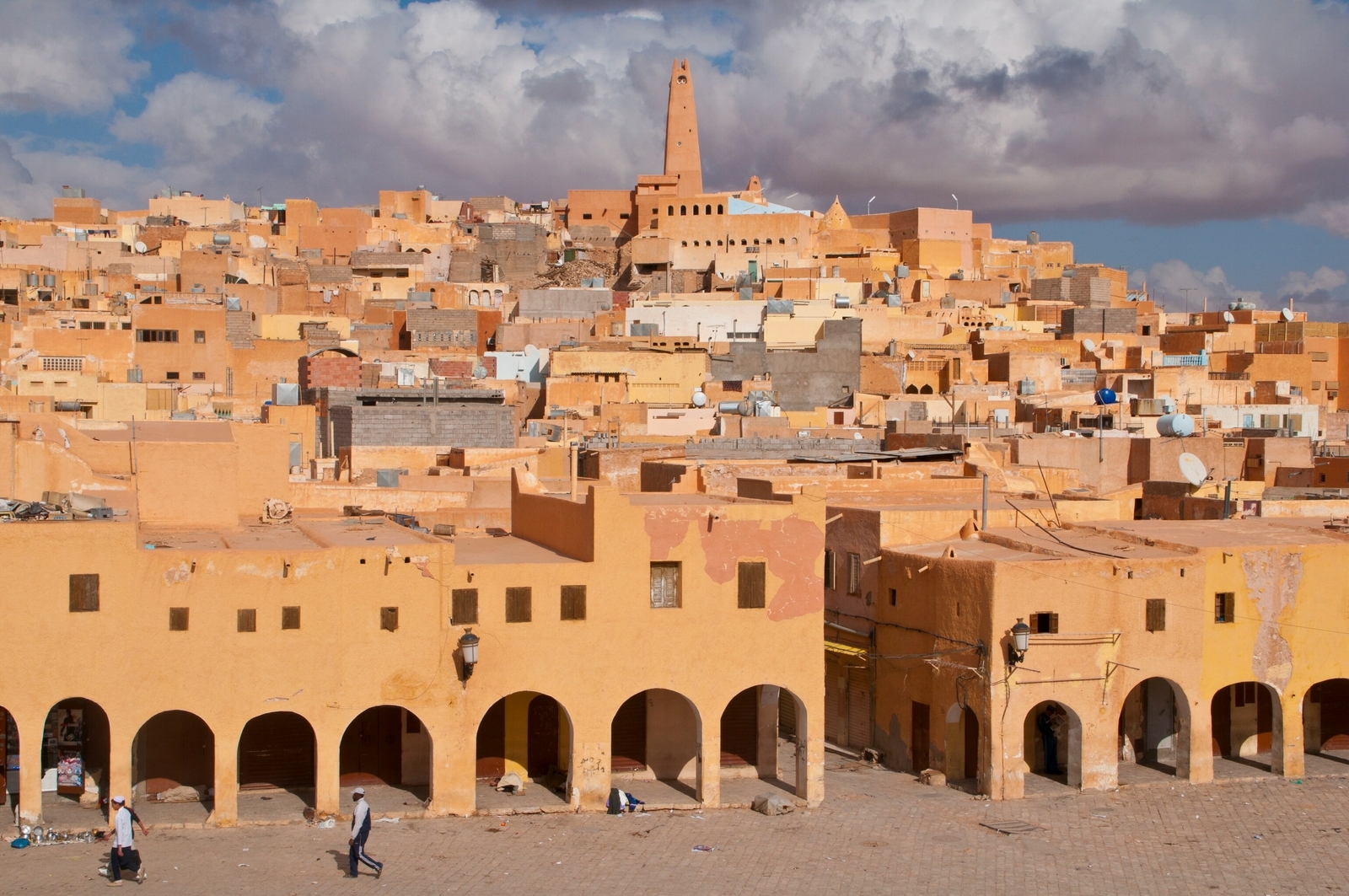
Ghardaïa is both the capital of the wilaya and the main city in the region. It is situated in the M'zab Valley, an oasis in the heart of the desert. The city is famous for its unique architecture and preserved traditional way of life. It is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage site as part of the "M'zab Valley Ancient Towns" site.
The wilaya of Ghardaïa offers spectacular desert landscapes, with sand dunes, lush palm groves, and traditional fortified villages called "ksour." The ksour of M'zab, such as Beni Isguen, Melika, and Ghardaïa, are must-visit tourist sites, providing an authentic experience of local architecture and culture.
The population of the wilaya of Ghardaïa is predominantly Berber, with a strong preservation of the Amazigh language and culture. Agriculture, particularly date and cereal cultivation, is one of the main economic activities in the region. Tourism also plays a significant role, attracting visitors who wish to discover the traditional way of life and unique architecture of the M'zab.
In terms of climate, the wilaya of Ghardaïa is characterized by a hot desert climate, with high temperatures in summer and mild winters.
In summary, the wilaya of Ghardaïa is a region located in southern Algeria, renowned for its unique architecture, preserved traditional way of life, and spectacular desert landscapes. It offers a cultural immersion into Berber culture and an authentic experience of life in a desert oasis.